AI could be the key to finding new drugs faster and cheaper. Many industries are trying to use AI for everything, but not all of them succeed. However, AI might have a real benefit for one area: drug discovery. AI could help speed up the long and costly process of making new medicines.
Finding new drugs is very hard and risky. It takes years to come up with a good idea and test it in the lab. Most of the time, the idea fails and the money is wasted. A study in 2022 showed that 90 percent of drug projects fail in clinical trials, after spending more than $2 billion each. This means that only a few drugs can make it to the market, and they have to cover the losses of the others. This also means that some diseases that affect fewer people get less attention.
AI is transforming the field of drug discovery by helping researchers find, test, and optimize new molecules and treatments. For example, Benevolent‘s VP of AI, Dr. Nicola Richmond, said that AI can speed up the process of finding the best molecules for a disease and making them into a form that patients can take. Recursion’s co-founder, Dr. Chris Gibson, said that AI can also save time by testing hundreds of options at once and finding the ones that work.
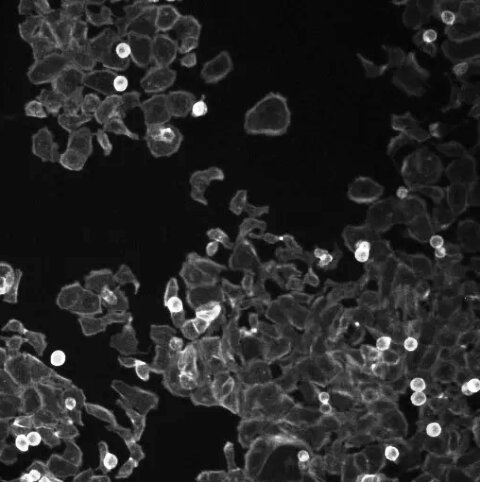
Dr. Anne E. Carpenter, a scientist at the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard, has developed a way to use AI to study cells. She uses dyes and software to make the cells visible and analyze millions of images of them. This can help researchers see how cells change in response to diseases and treatments, and find new connections that AI can use to discover new drugs.
AI can use patterns to find new drugs
AI is not only good at recognizing faces, but also at finding new ways to treat diseases. By using images of cells, AI can spot the differences between healthy and sick cells, and find the best chemicals to fix them.
Dr. Anne E. says that humans can sometimes tell if someone has a disease just by looking at their face. For example, some people with Down syndrome have a distinctive facial appearance. Doctors can also diagnose some diseases by looking at the cells under a microscope. But a computer can do this much faster and more accurately, and find patterns that humans might miss.
Dr. Carpenter says that by using images of cells, AI can find out how different chemicals affect them. For example, she can treat the cells with 100,000 different chemicals, one by one, and see how they change. Then, she can use AI to group the chemicals based on how similar they are.
She says that this can help find new drugs for diseases. Sometimes, two chemicals that look similar can have the same effect on a cell, and maybe on a disease. But one of them might have fewer side effects than the other, or be cheaper, or easier to make. This way, AI can help find the best option.
She also says that AI can help discover new things about diseases. Sometimes, AI can find a group of genes that are related to a disease, but one of them is unknown. This can give a clue about what that gene does, and how it is involved in the disease. Maybe that gene is a good target for a new drug, and AI can help find the right chemical to bind to it.
Ai can use questions to find new drugs
Benevolent is a company that uses AI to find new drugs for diseases. Its VP of AI, Dr. Nicola Richmond, explains that they first select a disease that they want to treat. Then, they formulate a question about the disease mechanism or the potential intervention. For instance, they could ask if improving the cellular cleaning process could treat ALS, a fatal nerve and muscle disorder. (This is not a real project, just an example.) Next, they use AI to search for the best molecules that can answer their question. They also use AI to convert those molecules into a form that patients can take, and check if they are effective and safe. This can speed up the drug discovery process and reduce the costs.

AI has a lot of promise for drug discovery, but also many challenges and uncertainties. How much can we trust AI to find new medicines without human guidance? How can we ensure that the data and algorithms used by AI are reliable and fair? Dr. Richmond and Dr. Carpenter pointed out some of the limitations and biases in the current data sources, such as the lack of diversity and representativeness of cell samples and human participants. They also faced constraints in terms of resources and time to conduct their research. Ideally, they would like to have more data and more experiments to validate their findings.
We are still waiting for the outcomes of the first trials that use AI for drug discovery. We hope that they will be successful and lead to better treatments for patients. AI could potentially improve the efficiency and effectiveness of drug discovery, as well as reduce the costs and risks involved. This could open up new opportunities for tackling diseases that are currently neglected or underserved by the existing system. However, we also need to be cautious and realistic about the potential of AI, and not fall for the hype or false hopes. AI is not a magic solution, but a powerful tool that needs to be used wisely and ethically.





